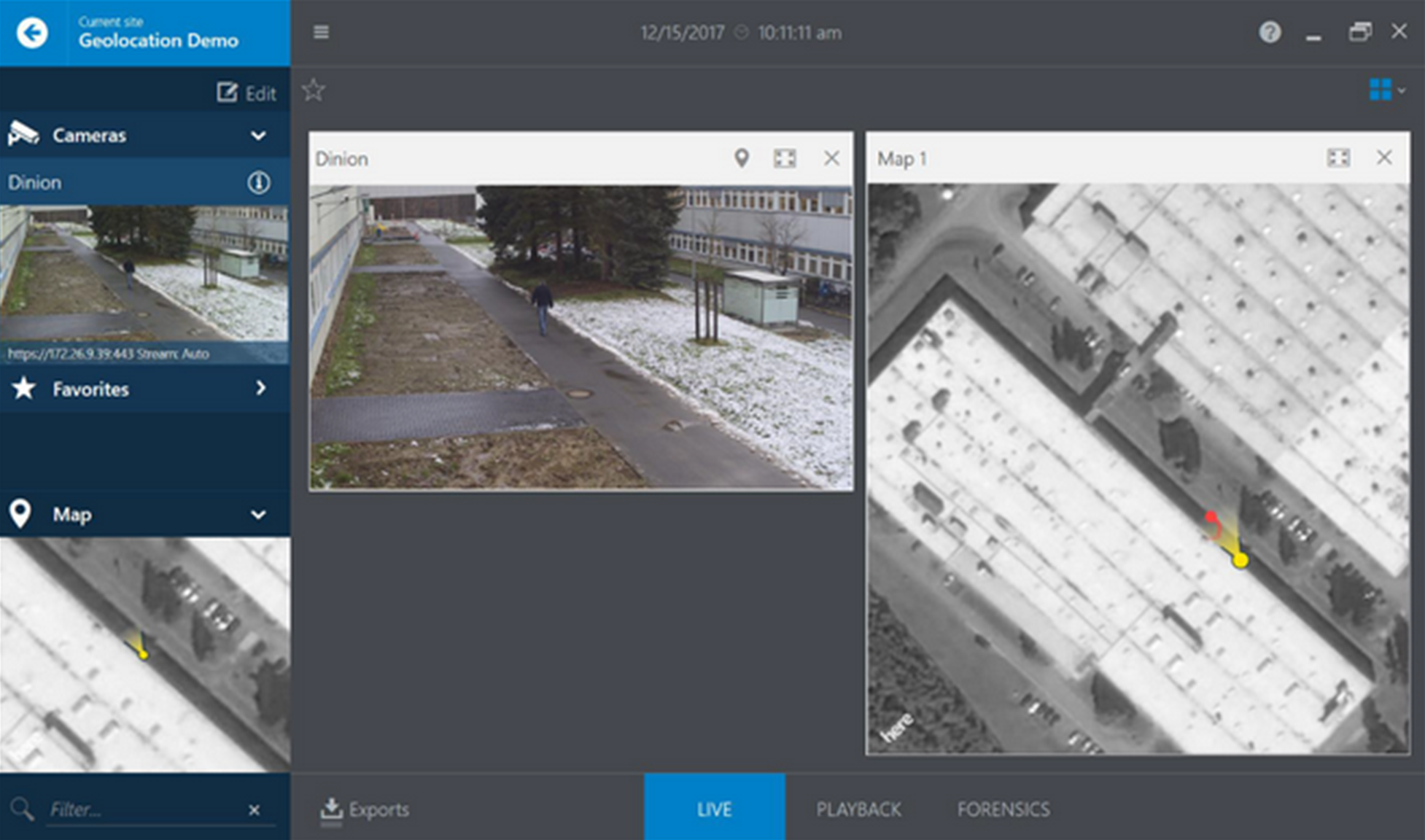
Geolocation plays a vital role in modern video surveillance systems, allowing for the precise identification and tracking of objects in real-world locations. In the case of Bosch cameras, geolocation refers to not only the position of the camera itself, but also the accurate tracking and detection of objects through the use of Intelligent Video Analytics (IVA) Pro. This advanced technology enables the camera to determine the exact coordinates of both the camera and the objects it tracks, whether it's through the global positioning system (GPS) or a local map coordinate system.
However, to ensure the full effectiveness of geolocation, it is essential to calibrate the camera accordingly. Calibration ensures that the camera is accurately aligned with its surroundings and enables it to determine the positions of both itself and the detected objects with precision. Map-based calibration emerges as an ideal solution in this context. By utilizing maps and their associated coordinates, the camera can establish precise geolocation data, facilitating seamless tracking and identification.
The integration of map-based calibration with Bosch cameras allows for easy compatibility and integration with existing mapping systems. This calibration process optimizes the camera's geolocation capabilities, providing real-time and accurate data for surveillance and security purposes.
Geolocation in Bosch cameras includes the positioning of the camera itself, as well as the tracking and detection of objects using Intelligent Video Analytics (IVA) Pro. Calibration, specifically map-based calibration, is a crucial step in enabling geolocation functionality. By leveraging maps and precise coordinates, the camera can accurately determine its own position and the positions of the objects it tracks. This integration between geolocation and map-based calibration ensures the utmost accuracy and reliability in surveillance systems, enhancing security and situational awareness.
Camera Configuration Process >>
To start map-based calibration, open Configuration Manager, select a camera, and go to General > Camera Calibration.
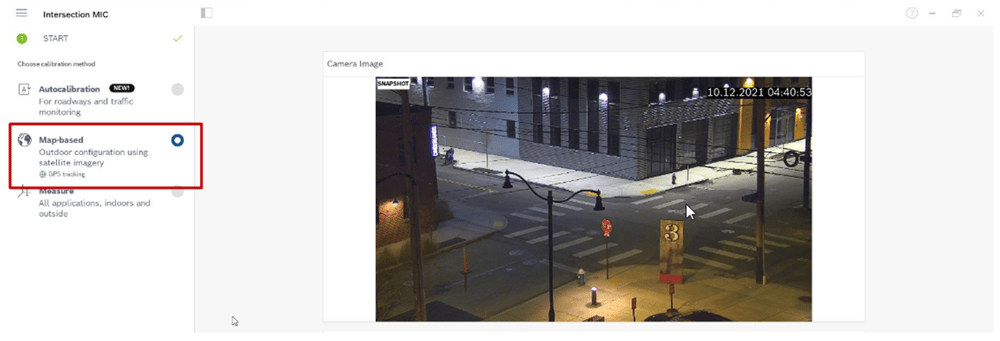
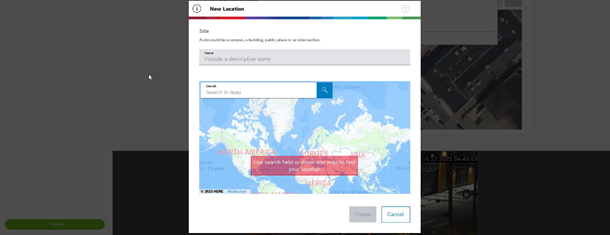
Next, select the area where the camera is located using the world map, which can be done by entering the address or by exploration.
Rotate and zoom the map until it is aligned with the camera image by using the mouse wheel or the buttons at the bottom of the map.
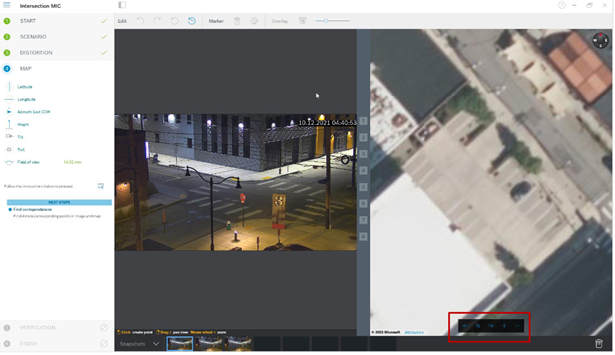
Click on the numbers between the camera image and the map and drag them into both the map and camera image. These are the markers. Choose corners on which to place the markers for the best accuracy. Ensure that each marker is placed at the same position on the camera image and on the map. Distribute the markers throughout the image.
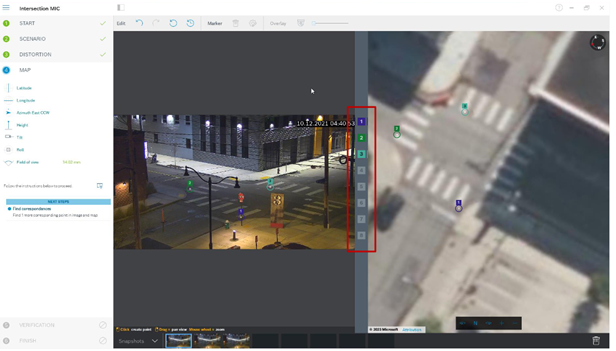
When enough camera markers have been placed, the calibration is automatic, and the camera image will be projected onto the map. Use the Overlay slider to make the projection more or less transparent to see how well it fits onto the map. If greater accuracy is needed, adjust the markers on the map.
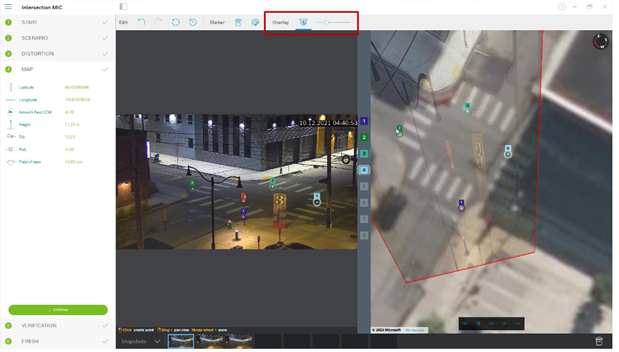
Once completed, click Finish and write the parameters to the camera.
Verifying accuracy
Once the map-based calibration is completed, accuracy can be tested by placing a person or car on the camera image and the map simultaneously to see if its size or position is correct. Ground distances or height above ground plane can also be measured, and the results will be displayed simultaneously in the camera image and map.
Featured white paper
 A white paper offers detailed information on Intelligent Video Analytics calibration and geolocation for cameras running firmware versions 8.47 and 8.80, using Configuration Manager version 7.70. It provides information on when calibration is needed, the various types, including Autocalibration, map-based, and assisted, and more.
A white paper offers detailed information on Intelligent Video Analytics calibration and geolocation for cameras running firmware versions 8.47 and 8.80, using Configuration Manager version 7.70. It provides information on when calibration is needed, the various types, including Autocalibration, map-based, and assisted, and more.
Need assistance?
Our team is ready to assist you with camera system design and a proof of concept demonstration.
Contact us here to discuss and schedule >>







